Electrical Engineering, B.S.
Learn to understand, design and develop devices and systems that operate on or generate electricity
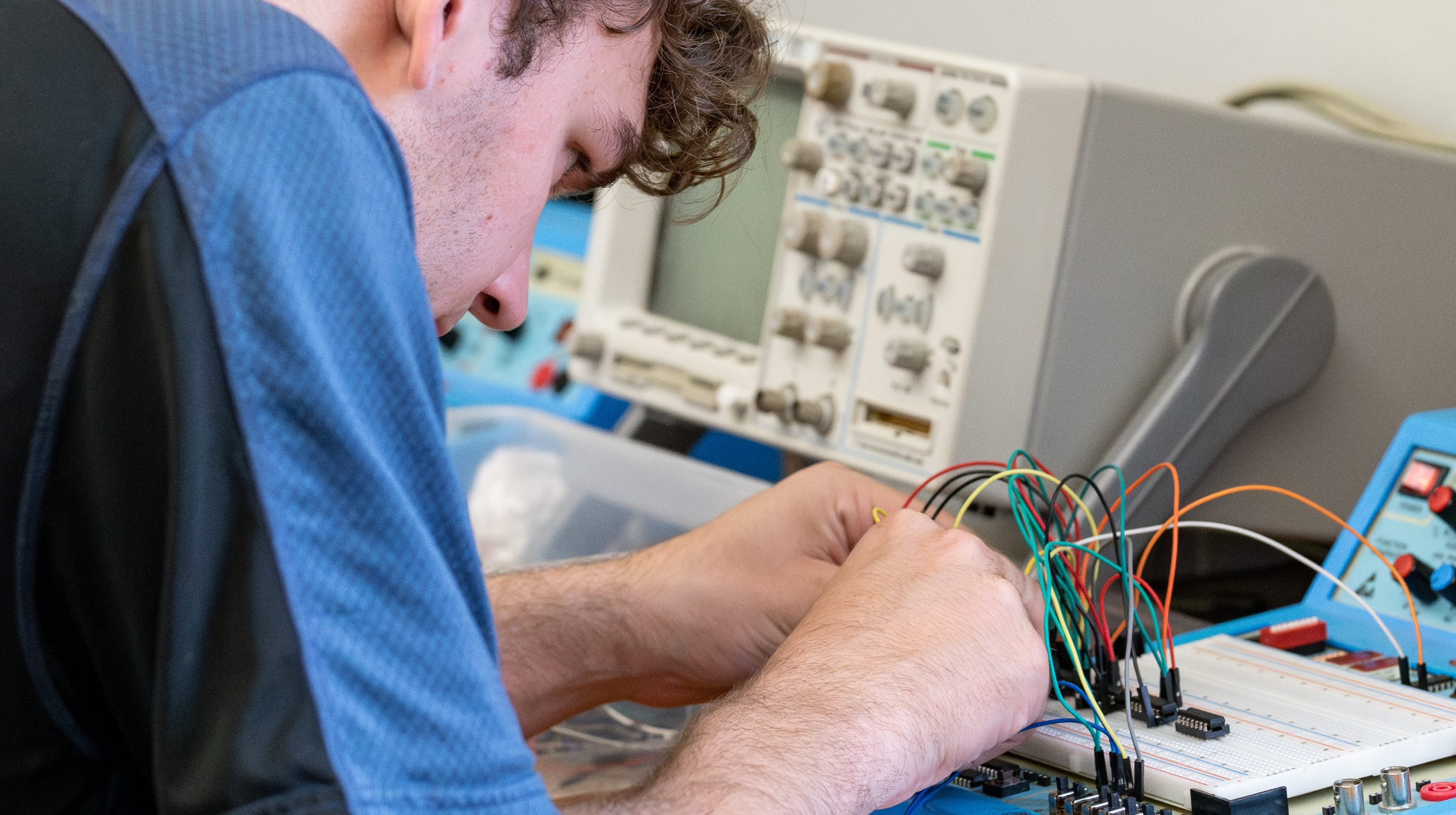
About the Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineers use the physics and mathematics of electricity, electromagnetism and electronics to create, develop and test electrical equipment and systems.
With an electrical engineering degree from Ole Miss, you will be set for a career in areas as diverse as the automotive, chemical and petroleum industries; power utilities; defense and aeronautics; and telecommunications and computers.
What you’ll find at Ole Miss
We are a tight-knit electrical engineering department, so you’ll enjoy:
Strong faculty interaction – with only 12 students for every professor in our upper-level classes.
Research opportunities – you can work with our faculty and graduate students on research areas such as electromagnetics and communications.
Access to innovation – we are a partner institution in the Broadband Wireless Access and Applications Center, sponsored by the National Science Foundation.
On this Page…
Program Information
Degree
B.S.E.E. in Electrical Engineering
Emphases
Standard track only
Required Credit Hours
128
Program Type
Major
Program Location
School
Duration
4 years
Beyond the classroom
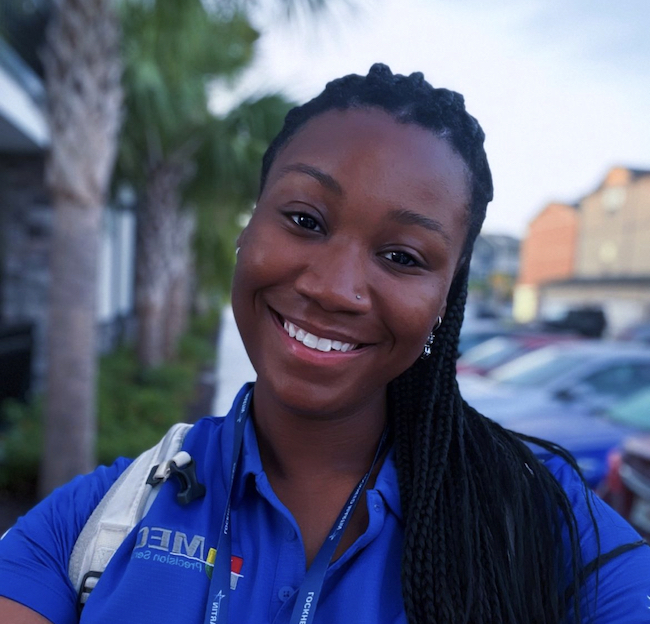

Co-ops and internships
Work for a semester or the summer in a company or lab to see what electrical engineers do.
Photo: Electrical engineering student Madison Page spent the summer of 2023 working at Lockheed Martin as a test engineering intern.

Research
Help our professors in their research efforts – looking into broadband wireless, space systems, defense, environmental monitoring, and more.
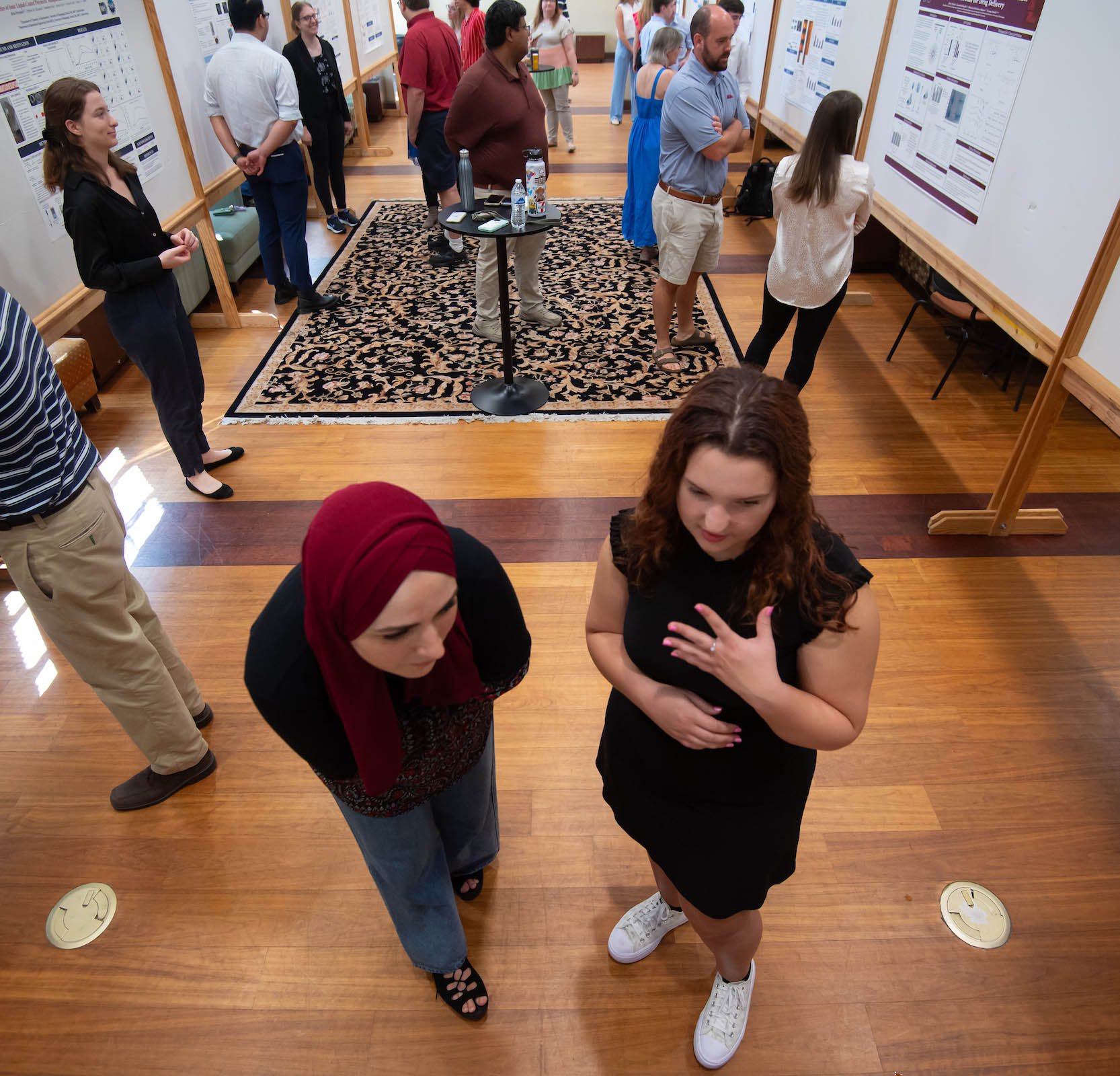

Student organizations
Join a club or learn more about your field in the Association for Computing Machinery or Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers.
Next Steps
Explore Affordability
We have a variety of scholarships and financial aid options to help make college more affordable for you and your family.
Apply to the University of Mississippi
Are you ready to take the next step toward building your legacy?
